What’s FOS?
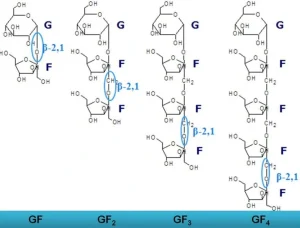
FOS (Fructo-oligosaccharides) is a mixture of oligosaccharides (GF2, GF3, GF4) which are composed of fructose units connected by ß (2-1) links. These molecules are terminated by a fructose unit. The total number of fructose or glucose units (Degree of Polymerization or DP) of oligofructose ranges mainly between 2 and 4.
Chemical structure of FOS
Production of FOS
FOS obtained by Enzymatic Synthesis of sucrose.
Physiological properties of FOS
FOS is prebiotic, a non-digestible food ingredient that affects the host beneficially by selectively stimulating the growth and/or activity of bacteria in the colon. In vitro tests have found that FOS are excellent and selective growth media and energy substrates for Bifid bacteria. These bacteria have been shown to inhibit the development of a number of harmful strains. The results of these studies have been confirmed in numerous clinical human studies.
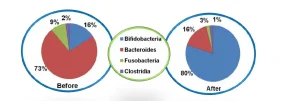
Enhance the absorption of mineral

Processing properties of FOS as an Ingredient
∗ Sweetness of FOS is 0.3-0.6 times of sucrose.
∗ FOS is very soluble in water and more soluble than sucrose.
∗ It does not crystallize, precipitate or leave a dry or sandy feeling in the mouth.
∗ Viscosity is relativity higher than sucrose.
Stability of FOS
In very acid conditions, significant exposure times and temperatures, FOS may hydrolyse into fructose. FOS is more sensitive to acid hydrolysis. This makes the use of FOS in highly acidic ambient products with a long shelf life such as soft drinks rather difficult. In most other applications, such as industrial fruit preparations and fresh fruit juices, the hydrolysis can be limited by controlling the process.